What is norepinephrine responsible for?
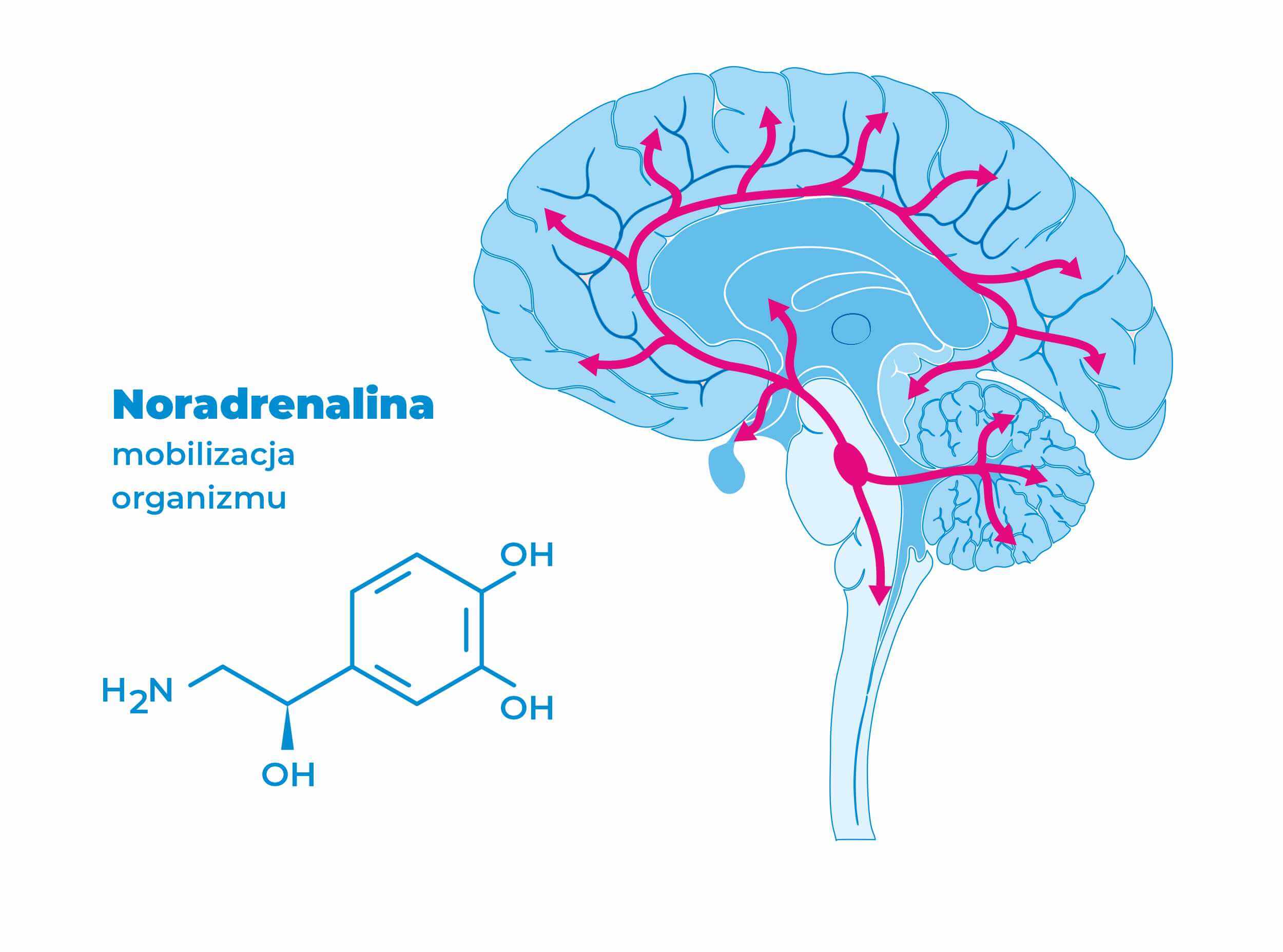
Noradrenaline is responsible for increasing attention and strengthening alertness when the nervous system is in a state of arousal. In addition, noadrenaline increases blood pressure, relaxes the bronchi and reduces intestinal peristalsis.
What are the effects of a deficiency or low level of norepinephrine?
The primary effect of deficiency or low levels of norepinephrine is tachycardia. In addition, norepinephrine deficiency can lead to hypotension and chronic fatigue. Low levels of norepinephrine also cause difficulties with weight loss, but above all serious mood and sleep disorders.
What are the effects of excess or high levels of norepinephrine?
The primary effect of excess or high levels of norepinephrine is bradycardia. In addition, high levels of noradrenaline can cause hypertension, dizziness and visual disturbances. It also causes unjustified anxiety. Often people with too much norepinephrine will experience physical and mental exhaustion. In addition, noradrenaline contributes to anxiety disorders and mood disorders, as well as difficulty falling asleep and staying asleep.
How to increase the secretion of norepinephrine?
The secretion of noradrenaline can be increased by increasing physical exercise and supplementing with vitamin C and B vitamins, especially B2, B6 and B12. In addition, the secretion of adrenaline is stimulated with drugs.
How to reduce the secretion of norepinephrine?
You can reduce the secretion of noradrenaline by leading a quiet lifestyle poor in foods containing tyrosine. In addition, avoiding caffeine helps to reduce the level of norepinephrine in the blood.